
During March 2021, the widening availability of COVID-19 vaccinations, signs of improving economic conditions, and a third, $1.9 trillion stimulus package brought about more optimistic growth projections. Even though a healthy economy could be good news for many businesses and the financial markets, rising inflation expectations caused a multi-week sell-off in U.S. government bonds that pushed up longer-term yields and sent the Nasdaq Composite Index into correction territory on March 8, 2021.1
Promising a patient approach, the Federal Reserve stated that it would not raise interest rates until the labor market fully recovers and inflation moderately exceeds the 2% target for some time.2 But some investors worry that sharply higher inflation could force policymakers to boost rates sooner than originally expected.
Here’s a closer look at some specific types of investment risk that could influence individual stock prices and/or cause broader market swings during the second half of 2021.
Inflation and Interest-Rate Fears
Inflation and interest rates are two different but closely related investment risks. The Federal Reserve is tasked with fostering full employment and controlling inflation. One way it balances these two goals is by lowering interest rates to stimulate business activity or raising rates to help slow inflation when the economy is heating up too fast.
High inflation erodes the value of investment returns, but when interest rates rise, bond values fall (and vice versa). These risks are obvious considerations for bond owners, but they also impact stocks. When goods, services, and credit cost more, consumers have less purchasing power, which can hurt company earnings and stock prices as well.
Rising bond yields might continue to have a negative effect on stock values, because as they move up, borrowing costs for most businesses also rise, cutting into profits. Higher yields could also entice risk-averse investors to sell their stocks and buy more stable bonds instead.
Legislative or Regulatory Impacts
Some government actions (such as antitrust lawsuits, higher taxes, and more stringent regulations or standards) make it more difficult and expensive for companies to do business, which can adversely affect their earnings and stock prices. On the other hand, government subsidies and tariffs on foreign products can provide competitive advantages.
The Justice Department, Federal Trade Commission, and numerous states are in the midst of antitrust lawsuits or major investigations into the business practices of several market-dominating tech companies.3 In another example, the Securities and Exchange Commission is considering new standards for corporate disclosures related to environmental, social, and governance risks.4
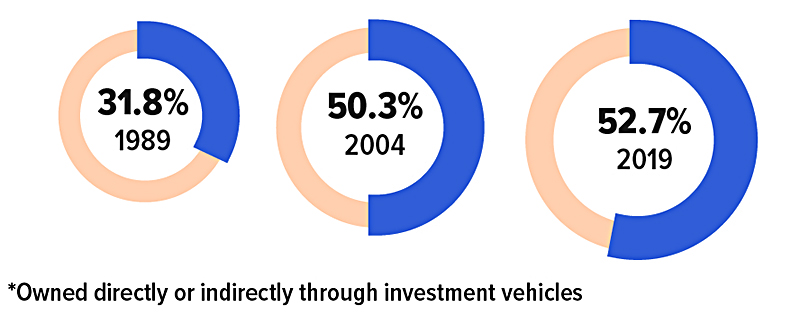
Percentage of U.S. Households Who Own Stocks*
Event or Headline-Driven Volatility
Headline risk refers to the possibility that events reported in the media could hurt a company’s reputation and/or earnings prospects. Troubling news can cause market backlash against a specific company or an entire industry. Companies try to manage this risk through public relations campaigns and other efforts to generate positive news that leaves a good impression on consumers. Events that threaten to disrupt business activity nationwide, regionally, or around the world can cause sudden stock market declines.
The market responds to news, good or bad, almost every day. For this reason, your portfolio should be designed to weather a range of market conditions and have a risk profile that reflects your ability to endure periods of market volatility, both financially and emotionally.
The principal value of bonds may fluctuate with changes in interest rates and market conditions. Bonds redeemed prior to maturity may be worth more or less than their original cost. The return and principal value of stocks fluctuate with changes in market conditions. Shares, when sold, may be worth more or less than their original cost. Investments seeking to achieve higher yields also involve a higher degree of risk.1) The Wall Street Journal, March 8, 2021
2) Federal Reserve, March 17, 2021
3) Reuters, December 16, 2020
4) The Wall Street Journal, February 24, 2021
Prepared by Broadridge Advisor Solutions Copyright 2021.
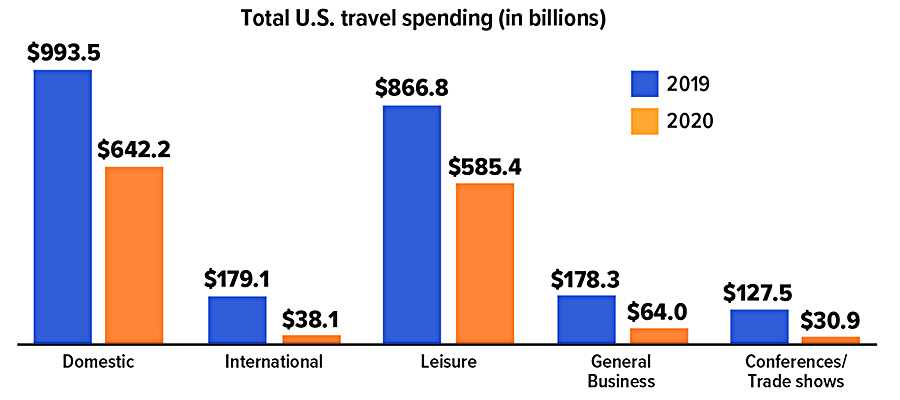
The pandemic hit the travel industry especially hard during 2020.
The U.S. travel industry’s total economic output plummeted 42% in 2020. A full 65% of all jobs lost in the United States were those supported by the travel industry. Perhaps unsurprisingly, the hardest-hit areas were business travel, particularly spending related to conferences, conventions, and trade shows, as well as international travel.
Federal, state, and local government coffers were also strained, as travel-related taxes fell by 34%.
Total travel spending in the United States, accounting for both domestic and international travelers, is expected to rise by 23.6% in 2021.
Prepared by Broadridge Advisor Solutions Copyright 2021.

The housing market during the coronavirus pandemic has certainly been notable. Historically low interest rates resulted in record homebuying, even as housing prices escalated.1
Fortunately, the mortgage industry has been able to keep up with the pace of the real estate market by utilizing already existing technology. Homebuyers can search for lenders, compare interest rates, and apply for mortgages online. In addition, mortgage lenders are able to do alternative appraisals, perform safe home inspections, and conduct closings electronically.
Even though applying for a mortgage is much easier these days, navigating the world of mortgages — especially for first-time homebuyers — can be complicated. As a result, you’ll want to keep the following tips in mind.
Check and maintain your credit. A high credit score not only may make it easier to obtain a mortgage loan but could potentially result in a lower interest rate. Be sure to review your credit report for inaccuracies. You may have to take steps to improve your credit history, such as paying your monthly bills on time and limiting credit inquiries on your credit report (which are made every time you apply for new credit).
Shop around. Be sure to shop around among various lenders and compare the types of loans offered, along with the costs and rates associated with those loans. Consider each lender’s customer service reputation as well.
Get pre-approved for a loan. In today’s hot housing market, it’s essential to have a mortgage pre-approval letter in hand before making an offer. Obtaining a mortgage pre-approval letter lets you know how large a loan you can get. However, this isn’t necessarily how much you can afford. Be sure to examine your budget and lifestyle to make sure that your mortgage payment — principal and interest as well as property taxes and homeowners insurance — is within your means.
Review your down-payment options. Though lenders prefer a down payment of 20% or more, some types of home loans allow down payments as low as 3%. A larger down payment can help you obtain a lower interest rate, potentially avoid paying for private mortgage insurance, and have smaller monthly payments.
Read the fine print. Before you sign any paperwork, make sure that you fully understand the terms of your mortgage loan and the costs associated with it. For example, if you are applying for an adjustable-rate mortgage, it’s important to be aware of how and when the interest rate for the loan will adjust.
1) MarketWatch, September 5, 2020
Prepared by Broadridge Advisor Solutions Copyright 2020.

Every year, the Internal Revenue Service announces cost-of-living adjustments that affect contribution limits for retirement plans and various tax deduction, exclusion, exemption, and threshold amounts. Here are a few of the key adjustments for 2021.
Estate, Gift, and Generation-Skipping Transfer Tax
- The annual gift tax exclusion (and annual generation-skipping transfer tax exclusion) for 2021 is $15,000, the same as in 2020.
- The gift and estate tax basic exclusion amount (and generation-skipping transfer tax exemption) for 2021 is $11,700,000, up from $11,580,000 in 2020.
Standard Deduction
A taxpayer can generally choose to itemize certain deductions or claim a standard deduction on the federal income tax return. In 2021, the standard deduction is:
- $12,550 (up from $12,400 in 2020) for single filers or married individuals filing separate returns
- $25,100 (up from $24,800 in 2020) for married individuals filing joint returns
- $18,800 (up from $18,650 in 2020) for heads of households
The additional standard deduction amount for the blind or aged (age 65 or older) in 2021 is:
- $1,700 (up from $1,650 in 2020) for single filers and heads of households
- $1,350 (up from $1,300 in 2020) for all other filing statuses
Special rules apply if you can be claimed as a dependent by another taxpayer.
IRAs
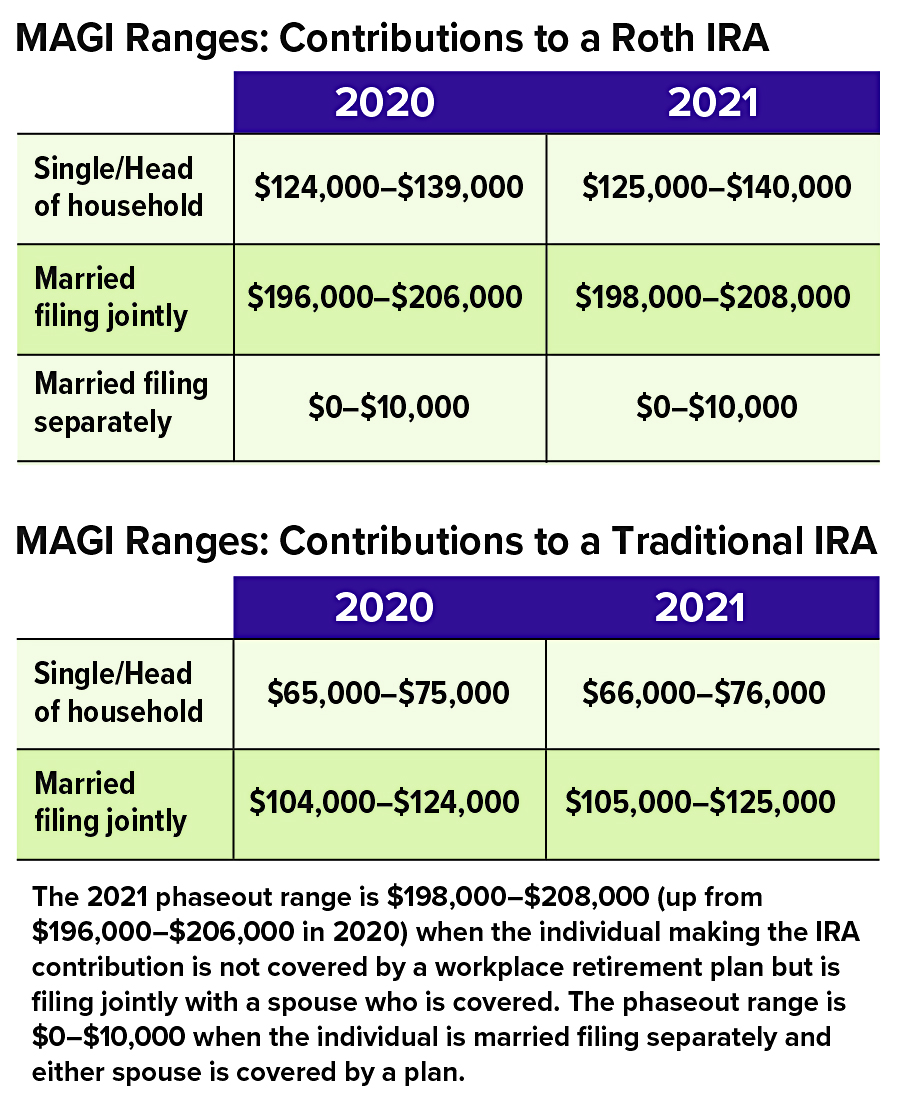
The combined annual limit on contributions to traditional and Roth IRAs is $6,000 in 2021 (the same as in 2020), with individuals age 50 and older able to contribute an additional $1,000. The limit on contributions to a Roth IRA phases out for certain modified adjusted gross income (MAGI) ranges. For individuals who are covered by a workplace retirement plan, the deduction for contributions to a traditional IRA also phases out for certain MAGI ranges. (The limit on nondeductible contributions to a traditional IRA is not subject to phase-out based on MAGI.)
Employer Retirement Plans
- Employees who participate in 401(k), 403(b), and most 457 plans can defer up to $19,500 in compensation in 2021 (the same as in 2020); employees age 50 and older can defer up to an additional $6,500 in 2021 (the same as in 2020).
- Employees participating in a SIMPLE retirement plan can defer up to $13,500 in 2021 (the same as in 2020), and employees age 50 and older can defer up to an additional $3,000 in 2021 (the same as in 2020).
Kiddie Tax: Child’s Unearned Income
Under the kiddie tax, a child’s unearned income above $2,200 in 2021 (the same as in 2020) is taxed using the parents’ tax rates.
Prepared by Broadridge Advisor Solutions Copyright 2020.

Tax filing season is here again. If you haven’t done so already, you’ll want to start pulling things together — that includes getting your hands on a copy of your 2019 tax return and gathering W-2s, 1099s, and deduction records. You’ll need these records whether you’re preparing your own return or paying someone else to prepare your tax return for you.
Don’t procrastinate. The filing deadline for individuals is generally Monday, May 17, 2021.
Filing for an Extension
If you don’t think you’re going to be able to file your federal income tax return by the due date, you can file for and obtain an extension using IRS Form 4868, Application for Automatic Extension of Time to File U.S. Individual Income Tax Return. Filing this extension gives you an additional five months (to October 15, 2021) to file your federal income tax return. You can also file for an extension electronically — instructions on how to do so can be found in the Form 4868 instructions.
Due Dates for 2020 Tax Returns

Filing for an automatic extension does not provide any additional time to pay your tax. When you file for an extension, you have to estimate the amount of tax you will owe and pay this amount by the May filing due date. If you don’t pay the amount you’ve estimated, you may owe interest and penalties. In fact, if the IRS believes that your estimate was not reasonable, it may void your extension.
Note: Special rules apply if you’re living outside the country or serving in the military and on duty outside the United States. In these circumstances, you are generally allowed an automatic one-month extension (to June 15, 2021) without filing Form 4868, though interest will be owed on any taxes due that are paid after the May filing due date. If you served in a combat zone or qualified hazardous duty area, you may be eligible for a longer extension of time to file.
What If You Owe?
One of the biggest mistakes you can make is not filing your return because you owe money. If your return shows a balance due, file and pay the amount due in full by the due date if possible.
If there’s no way that you can pay what you owe, file the return and pay as much as you can afford. You’ll owe interest and possibly penalties on the unpaid tax, but you’ll limit the penalties assessed by filing your return on time, and you may be able to work with the IRS to pay the remaining balance (options can include paying the unpaid balance in installments).
Expecting a Refund?
The IRS has stepped up efforts to combat identity theft and tax refund fraud. More aggressive filters that are intended to curtail fraudulent refunds may inadvertently delay some legitimate refund requests. In fact, the IRS is required to hold refunds on all tax returns claiming the earned income tax credit or the additional child tax credit until at least February 15.
Most filers, though, can expect a refund check to be issued within 21 days of the IRS receiving a tax return. However, note that in 2020 the IRS experienced delays in processing 2019 paper tax returns due to limited staffing during the coronavirus pandemic.
So if you are expecting a refund on your 2020 tax return, consider filing as soon as possible and filing electronically.
Prepared by Broadridge Advisor Solutions Copyright 2020.
